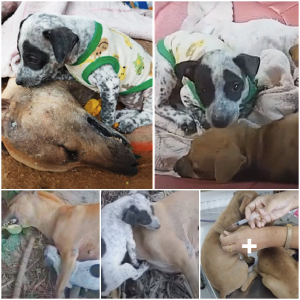
Mango worms, scientifically known as Cordylobia anthropophaga, are a type of parasitic larvae commonly found in tropical regions, particularly in sub-Saharan Africa. These larvae are the offspring of the mango fly and pose a significant health risk to dogs, causing discomfort and potential complications if left untreated. Understanding the symptoms, treatment options, and prevention methods is crucial for dog owners in areas where mango worms are prevalent.

Symptoms: Identifying mango worm infestation in dogs is essential for timely treatment. Common symptoms include:
- Visible Worms: The presence of small, white larvae protruding from the skin, typically in areas with little hair coverage such as the groin, armpits, or between toes.
- Itching and Irritation: Dogs may exhibit signs of discomfort, including excessive scratching, licking, or biting at the affected areas.
- Swelling and Inflammation: Infected areas may become swollen, red, and inflamed due to the body’s reaction to the presence of the larvae.
- Secondary Infections: Continuous scratching and biting can lead to open wounds, increasing the risk of bacterial infections.

Treatment: Prompt and appropriate treatment is essential for relieving the dog’s discomfort and preventing complications. Here are the steps typically involved in treating mango worm infestation:
- Manual Removal: Carefully extract each mango worm from the dog’s skin using sterilized tweezers or a specialized tool. It’s crucial to ensure complete removal to prevent any remaining larvae from causing further infestation.
- Antiseptic Cleansing: Cleanse the affected area with an antiseptic solution to reduce the risk of secondary infections and promote healing.

- Topical Treatment: Apply topical medications or ointments prescribed by a veterinarian to alleviate itching, reduce inflammation, and promote healing of the affected skin.
- Oral Medication: In severe cases or if secondary infections have developed, veterinarians may prescribe oral antibiotics or anti-inflammatory drugs to address underlying issues and support the dog’s recovery.
Prevention: Preventing mango worm infestation in dogs requires proactive measures, especially in areas where the parasites are endemic. Here are some preventive steps dog owners can take:
- Regular Grooming: Maintain good hygiene by regularly grooming your dog, including thorough brushing and bathing to remove dirt, debris, and potential parasites from the coat.
- Environmental Control: Keep your dog’s living environment clean and free of organic debris, which may attract mango flies and their larvae.
- Protective Measures: Use insect repellents or protective clothing, such as insect-repellent collars or vests, when taking your dog outdoors in areas where mango worms are prevalent.
- Vigilant Inspection: Routinely inspect your dog’s skin, especially after outdoor activities, for any signs of mango worm infestation. Early detection allows for prompt treatment and prevents the infestation from worsening.

In conclusion, mango worm infestation can pose a significant health concern for dogs in tropical regions. By recognizing the symptoms, seeking timely treatment, and implementing preventive measures, dog owners can effectively manage and reduce the risk of mango worm infestation, ensuring the health and well-being of their canine companions. Consulting a veterinarian for professional guidance and treatment is crucial for addressing any concerns related to mango worm infestation in dogs.