 Mangoworms, also known as cord worms, pose a common concern among pet owners, particularly those with dogs. These parasites, prevalent in warm and humid climates, can cause significant discomfort and health issues if left untreated.
Mangoworms, also known as cord worms, pose a common concern among pet owners, particularly those with dogs. These parasites, prevalent in warm and humid climates, can cause significant discomfort and health issues if left untreated.
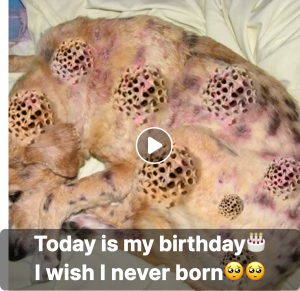
Mangoworms are the larvae of the mango fly, which burrow under the skin of animals, including dogs, where they develop and grow. Often found in areas of the body where the skin is thin, such as the abdomen, ears, neck, and legs, these parasites can lead to various symptoms in infected dogs.

Symptoms of a mangoworm infestation in dogs can vary but typically include intense itching, redness, and inflammation at the site of infection. Infected dogs may also excessively lick, bite, or scratch in an attempt to alleviate the discomfort caused by the worms.
It is crucial for pet owners to remain vigilant for signs of a mangoworm infestation and seek immediate veterinary treatment if they suspect their dog is infected. A veterinarian can diagnose the infestation through a physical examination and, if necessary, may conduct additional tests such as blood analysis or skin scraping.

Treatment for mangoworms in dogs usually involves the extraction of larvae from beneath the skin, followed by cleaning and disinfecting the affected area. In severe cases, medication may be administered to control infection and relieve the dog’s inflammation and discomfort.
In addition to medical treatment, preventive measures are essential to protect dogs from mangoworm infestations. This may include the use of appropriate insect repellents, keeping the dog’s living area clean and clear, and avoiding exposure to areas where mango flies are prevalent.

In summary, mangoworms present a significant health concern for dogs, but with early detection and proper treatment, affected dogs can fully recover. However, prevention remains the best strategy for safeguarding pets from this potentially dangerous parasitic infestation.





