The terror of “mangoworms” in dogs: A global threat that causes concern
In recent years, an emerging threat has been stalking man’s best friends around the world: mangoworms. These tiny parasites, known scientifically as Cordylobia anthropophaga, are wreaking havoc on the health of dogs, causing concern and alarm among pet owners and veterinary professionals alike.
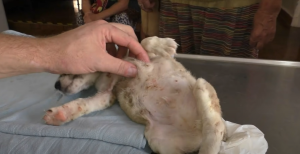
Mangoworms are larvae of the tumbu fly, commonly found in tropical and subtropical areas of Africa and some parts of Asia. They feed on the living flesh of mammals, including dogs, and their life cycle begins when female flies lay their eggs in the soil or on the fur of animals. Once the eggs hatch, the larvae burrow into the host’s skin, where they feed and grow, causing significant damage and intense pain.
Symptoms of a mangoworm infestation can range from itching and irritation to serious infections and systemic complications. Affected dogs may show signs of general malaise, loss of appetite, and in severe cases, the presence of visible bumps or skin lesions may be observed where the larvae are active.
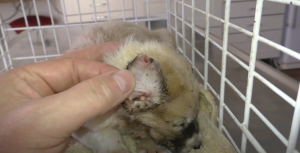
Treating mangoworms can be challenging and often requires immediate veterinary intervention. A variety of methods can be used, ranging from manual removal of the larvae to the use of antiparasitic medications and topical therapies to eliminate infestations and prevent recurrences.
As cases of mangoworms in dogs continue to rise around the world, it is crucial that pet owners keep an eye out for signs of infestation and take preventive measures to protect their furry companions. This includes keeping the pet’s environment clean, avoiding fly-infested areas, and performing regular skin and coat checks on dogs to detect the early presence of larvae.
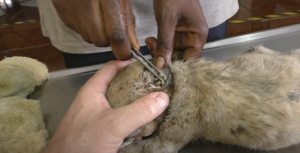
Ultimately, the fight against mangoworms requires collaboration between responsible owners, veterinary professionals, and global efforts to address the environmental conditions that favor the spread of these parasites. Only through collective action and continued commitment can we hope to mitigate this growing threat and protect the health and well-being of our beloved canine companions.
Video:





